Technology Platform CHyN Clean room
The technology platform CHyN clean room with focus on complex nanofabrication processes is a state-of-the-art clean room facility that’s designed as a clean room ISO-Class 4 standard – an ultra-clean, particle- and dust free user lab. Equipped with cutting-edge instrumentation, it provides an ideal environment for top-level interdisciplinary research.
The lab facility is jointly operated by three organizations – Universität Hamburg (UHH), Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (DESY) and Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter (MPSD). The lab is located within the Center for Hybrid Nanostructures (CHyN) Building 600 on the research campus, Science City Hamburg Bahrenfeld (SCHB).
Organization
The CHyN clean room is operated and managed by a coordinator, engineers and senior researchers from all the three organizations – UHH, DESY and MPSD – supervised by the clean room board. The board oversees the scientific directions and strategic development of the clean room.
The clean room coordinator serves as the central communication interface between users, staff, facility management, and the management board. Additionally, the coordinator oversees day-to-day operations and ensures smooth and efficient usage processes.
Content
Curious to know more about the CHyN clean room facility?
The CHyN clean room is structured into two main areas: the Yellow Room and the White Room, supported by associated user labs located outside the cleanroom complex. These labs enable advanced processing of extremely small structures down to 500 nanometers and below, high-resolution imaging, elemental analysis, and ion implantation.
The Yellow Room – Structuring at the Nanoscale
The Yellow Room is specifically designed for preparative synthesis processes such as wet-chemical processes and is also used for analytical work. It is particularly suited for lithographic structuring, conducted in a UV-protected environment. This allows for the fabrication of structures ranging from the sub-micrometer to the nanometer scale.
In addition to structuring, important material properties can be directly qualified in this area, including:
- surface roughness,
- thickness of deposited layers,
- and etch depth of structured materials.
The White Room – Deposition and Characterization of Functional Materials
Adjacent to the Yellow Room, the White Room focuses on the nano-deposition of various thin-film systems including:
- semi-conductor materials,
- functional materials such as bismuth or hafnium,
- insulating oxide or nitride layers for passivation,
- and metallic materials like gold, titanium, platinum, aluminum, or copper.
Moreover, the White Room enables dry etching for structural definition or patterning and optical characterization of deposited layers. These capabilities make it possible to design and transform materials into highly functional structures.
Access and staff team
Access and Usage of the CHyN clean room facility is a two-step process. After a short general safety introduction, process flow applications are submitted by respective research team and approved by the facility to ensure a safe and professional working environment. The facility is staffed with process instructors providing hands-on training and guiding the registered users on the proper operation of the complex equipment. Users can make independent bookings on the various equipment after completing the selected training sessions and subscription of the registered booking tool – cluster market – of the lab facility.
The dates and location for the scheduled monthly routine safety introduction could be downloaded here (click pdf file).
Contact
Should you require more information or interested in getting access to use the technology platform CHyN clean room, you could reach out to us through: chyn-cleanroom.min"AT"uni-hamburg.de
Dr. -Ing. Lewis Olaniyi Akinsinde
Coordinator Clean Room Technology Platform
Office: CFEL - Center for Free Electron Laser Science Hamburg, Building 99, Room O1.125
Luruper Chaussee 149
D-22761 Hamburg
Tel.: +49 (0)151 5538 8158
E-Mail: chyn-cleanroom.min"AT"uni-hamburg.de
For more information see the CHyN clean room homepage
Users
The users are mainly undergraduate students from the bachelor’s, and master’s to the PhD level, post-doctoral researchers, and senior scientists carrying out fundamental research in the fields of pharmacy, nanotechnology, biophysics, material science, microelectronics, life science, and quantum technology. Researchers from other discipline are also welcome.
Publications
2024
Haugg, S.; Mochalski, L. F.; Hedrich, C.; González Díaz-Palacio, I.; Deneke, K.; Zierold, R.; Blick, R. H. Field Emission from Carbon Nanotubes on Titanium Nitride-Coated Planar and 3D-Printed Substrates. Nanomaterials 2024, 14 (9), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090781.
2022
Haugg, S.; Hedrich, C.; Zierold, R.; Blick, R. H. Field Emission Characteristics of ZnO Nanowires Grown by Catalyst-Assisted MOCVD on Free-Standing Inorganic Nanomembranes. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2022, 55 (25), 255104. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac5d05.
Harberts, J.; Siegmund, M.; Hedrich, C.; Kim, W.; Fontcuberta i Morral, A.; Zierold, R.; Blick, R. H. Generation of Human IPSC-Derived Neurons on Nanowire Arrays Featuring Varying Lengths, Pitches, and Diameters. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9 (24), 2200806. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202200806.
Grote, L.; Seyrich, M.; Döhrmann, R.; Harouna-Mayer, S. Y.; Mancini, F.; Kaziukenas, E.; Fernandez-Cuesta, I.; A. Zito, C.; Vasylieva, O.; Wittwer, F.; Odstrčzil, M.; Mogos, N.; Landmann, M.; Schroer, C. G.; Koziej, D. Imaging Cu2O Nanocube Hollowing in Solution by Quantitative in Situ X-Ray Ptychography. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32373-2.
Esmek, F.M; Erichlandwehr, T; Brkovic, N; Pranzner, N.P; Teuber, J.P; Fernandez-Cuesta, I. Pillar-structured 3D inlets fabricated by dose-modulated e-beam lithography and nanoimprinting for DNA analysis in passive, clogging-free, nanofluidic devices. Nanotechnology 33, 2022, 385301, (12pp). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ac780d.
2021
Haugg, S.; Hedrich, C.; Blick, R. H.; Zierold, R. Subtractive Low-Temperature Preparation Route for Porous SiO2 Used for the Catalyst-Assisted Growth of ZnO Field Emitters. Nanomaterials 2021, 11 (12), 3357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123357.
2020
Harberts, J.; Haferkamp, U.; Haugg, S.; Fendler, C.; Lam, D.; Zierold, R.; Pless, O.; Blick, R. H. Interfacing Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons with Designed Nanowire Arrays as a Future Platform for Medical Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8 (9), 2434–2446. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0bm00182a.
2019
Esmek, F. M.; Bayat, P.; Pérez-Willard, F.; Volkenandt, T.; Blick, R. H.; Fernandez-Cuesta, I. Sculpturing Wafer-Scale Nanofluidic Devices for DNA Single Molecule Analysis. Nanoscale 2019, 11 (28), 13620–13631. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr02979f.
Harberts, J.; Zierold, R.; Fendler, C.; Koitmäe, A.; Bayat, P.; Fernandez-Cuesta, I.; Loers, G.; Diercks, B. P.; Fliegert, R.; Guse, A. H.; Ronning, C.; Otnes, G.; Borgström, M.; Blick, R. H. Culturing and Patch Clamping of Jurkat T Cells and Neurons on Al2O3 Coated Nanowire Arrays of Altered Morphology. RSC Adv. 2019, 9 (20), 11194–11201. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra05320k.
Hedrich, C.; Haugg, S.; Pacarizi, L.; Furlan, K. P.; Blick, R. H.; Zierold, R. Low-Temperature Vapor-Solid Growth of ZnO Nanowhiskers for Electron Field Emission. Coatings 2019, 9 (11), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9110698.
Fendler, C.; Denker, C.; Harberts, J.; Bayat, P.; Zierold, R.; Loers, G.; Münzenberg, M.; Blick, R. H. Microscaffolds by Direct Laser Writing for Neurite Guidance Leading to Tailor-Made Neuronal Networks. Adv. Biosyst. 2019, 3 (5), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.201800329.
List of Equipment
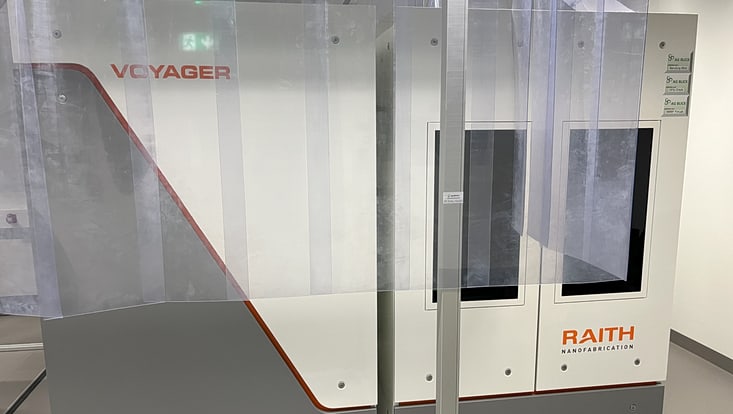

Photo: UHH/Akinsinde
Raith Voyager E-Beam Lithography System
Field of Application: The high-precision 50 kV electron beam lithography platform is for lithographic structuring purposes. The Voyager system has a nominal accuracy of 2 nm and a minimum feature size of 6 nm. The exposure of substrates sizes ranging from 5 mm to 4'' diameter is possible. Its recent software update automatic height sensing system allows optimized focus adjustment across the entire wafer surface, minimizing focus errors and stitching artifacts.
Location: EBL Voyager lab, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 063
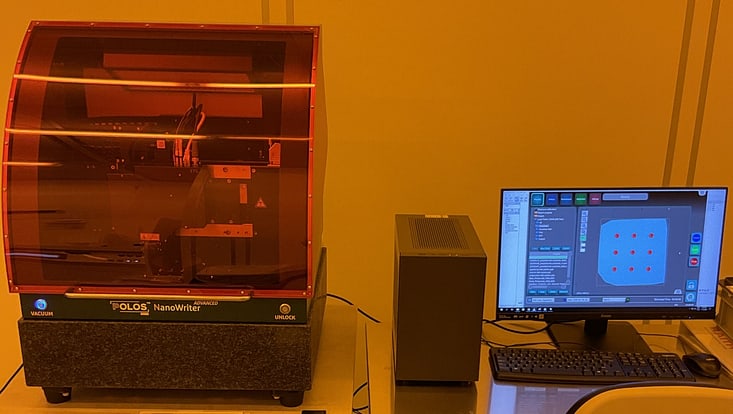

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Raith Picomaster: a high-resolution Maskless Laser Writing System
Field of Application: The PICOMASTER from Raith comprises an advanced laser lithography system engineered for high precision, maskless lithography applications.
Key Technical Specification:
Scan speed limits: maximum/ minimum scan speed of 200/20 mm/s for both directions with a wide movement range of 115 mm.
Step size: minimum step size of 5 nm for the scan axis and 20 nm for the step axis respectively. An optimal resolution as high as 2 nm is achievable.
XY-motion limits: the substrate size can vary from 5 x 5 to 125 x 125 mm2, and various substrate types (sapphire, Silicon, etc.,). The exposable area is 110 x 110mm2.
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 034
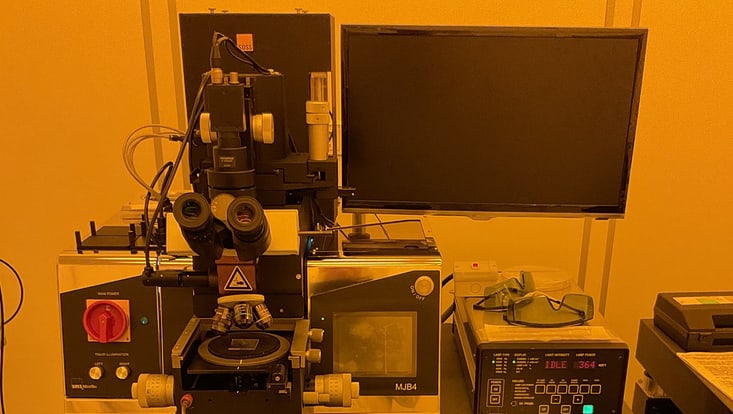
Photo: UHH/Stützle
UV Lithography Mask Aligner MJB4 from Karl Süss company
Field of Application: The MJB4 model Mask aligner is typically applied as a UV lithographic structuring. With it's equipped powerful 350W high pressure mercury lamp, the emission of two characteristics ultra-violett wavelength spectrum 365 nm and 313 nm useful for micro patterning are obtainable. Contacts and proximity exposure modes are possible. The smallest achievable feature size depends on the exposure mode: Hard contact roughly 1-micron, soft contact / proximity around 2 – 5 microns. Wafers and substrates size up to 100 mm (4”) diameter with uniformity in the exposure over a wide range are applicable.
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 034
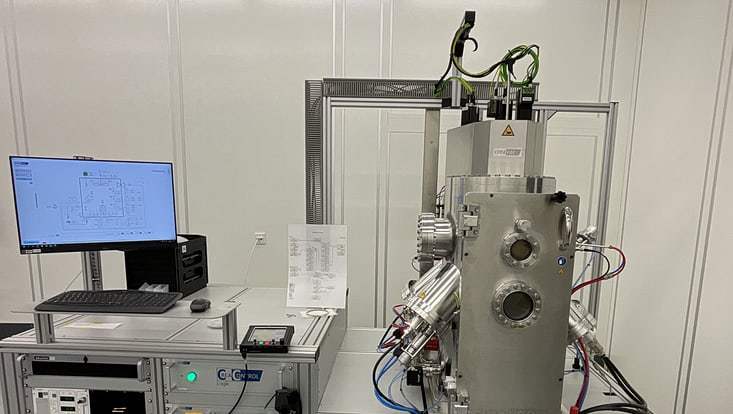
Photo: UHH/Stützle
High-vacuum Coating System from Creavac: Creamet 450 E-Beam S3 Coating System
Field of Apllication: The CREAMET 450 e-beam S3 from CREAVAC is a high-vacuum coating system that operates with a multi-pocket (6 pockets) electron beam evaporator and achieves a base vacuum of < 5 X 10⁻⁷ mbar to enable high quality hin-film deposition. Substrates up to 4'' can be optimally aligned using a rotating and tilting holder, ensuring uniform coatings. Additionally, three magnetron sputter sources are available, which can operate with RF, DC, and HiPIMS technology to evaporate various materials like Au, Ti, Pt etc. Furthermore, an ion beam source allows for targeted sputtering and control of the layer morphology.
Location: CHyN Clean room, White room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
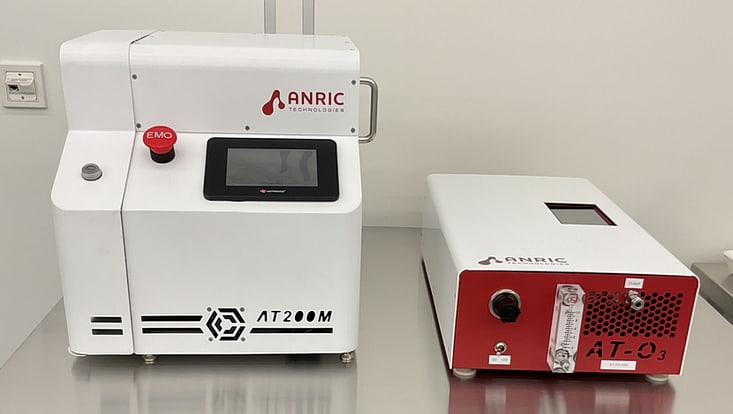

Photo: UHH/Stützle
AT200M Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) System
Field of Application: The ATM 200M is the smallest footprint ALD tool available on the market and is well-fitted for tabletop operation, and the small chamber size also ensures a high level of vacuum and small interaction volume during the deposition process. The system is equipped with one precursor and one counter-reactant, and all parts - precursor, manifold, chamber - can be heated to ensure no condensation. The deposition chamber is fitted for one 2” wafer and the deposition of thin film layers Si/SiO2, Hf/HfO2, Ti/TiO2, and Pt are possible. The typical deposition time for depositing e.g.standard recipe ca. 10nm Ti layer could last roughly 20 minutes.
Location: CHyN Clean room, White room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
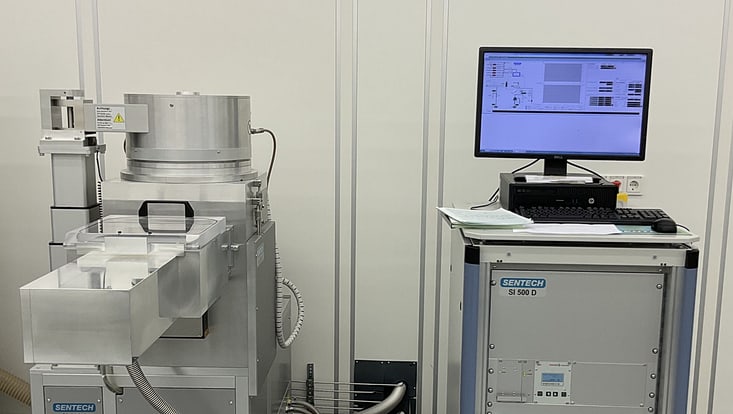

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Plasma Enhanced CVD Systems SI 500D 214 from Sentech
Field of Application: The inductively coupled plasma enhanced CVD (PECVD) system SI 500D 214 from Sentech is designed for high density, low ion energy, and low-pressure plasma deposition of dielectric thin films and low-damage, very low temperature deposition of passivation layers like nitrides. The attractiveness of low etch rate, high breakdown voltage, low stress, no damage of substrate facilitates an outstanding property of the deposited layers of thin film.
The key features and benefits of the PECVD system include reproducible processes that's achievable via fully controlled via systems and process gases are NH3, SiH4 in He, CF4, O2 and Ar.
Location: CHyN Clean room, White room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
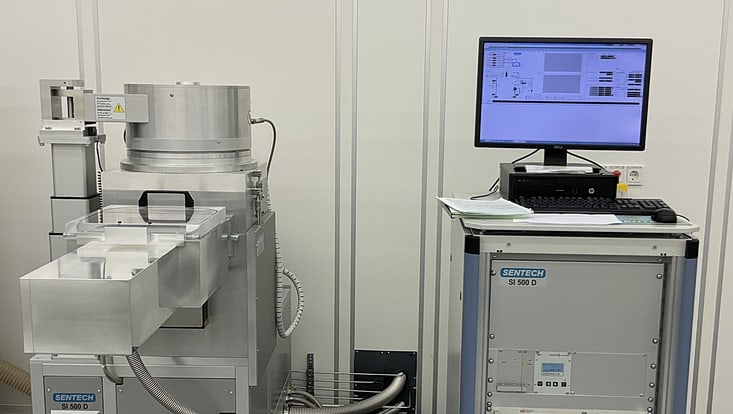

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Reactive Ion Etcher SI 500 215
Field of Applications: The SI 500 ICP-RIE from the company Sentech is a high-end plasma etch system that uses an inductively coupled plasma source with low ion energy for low-damage dry etch and nano structuring of different substrates mostly wafers, sapphire and glass. The system has its unique feature in processes reproducibility achievable through the integrated full controlled vacuum system, different levels of automation ranging from load-lock loading to the process chamber. The following standard reactive process gases SF6, CHF3, C4F8, O2 and Ar are utilized for the dry etching process.
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
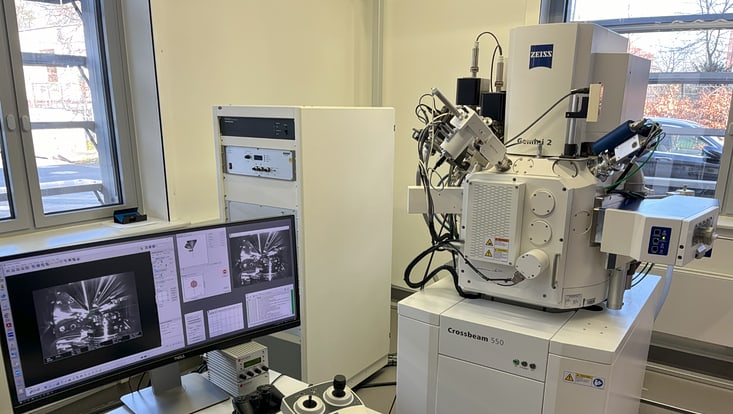

Photo: UHH/Akinsinde
FIB-SEM - ZEISS Crossbeam 550 coupled FIB
Field of Application: The FIB-SEM (ZEISS Crossbeam 550, is used in investigating the structure and morphology - high-resolution imaging with resolution below 10 nm of all kinds of conductive and non-conductive materials is possible - of different specimens by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) in combination with optional focused ion beam (FIB) milling for patterning purpose. Also, elemental analysis of the specimen material can be conducted by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The sample analysis enhanced by EDS to study the elemental composition and purity of thin films, micro- and -nanostructures.
Location: EBL Voyager lab, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 060
